Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency and how to prevent it?
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency in the body is the main cause of many diseases. Learn through the following article about the role of this vitamin and the risks of its deficiency in the human body and the reasons for that. Learn more about treatment and prevention methods with Ilagak Medical.
Definition of vitamin D deficiency

Vitamin D deficiency is a pathological condition that occurs when the level of vitamin D in the body decreases below the normal limit because the body is not exposed to the sun enough for vitamin D to be synthesized, or because there is a defect in the body that impedes the body’s ability to synthesize the vitamin. Vitamin D deficiency leads to the emergence of a group of neurological and psychological symptoms, as well as symptoms in the muscles, bones, and others.
What is the role of vitamin D in the body?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is important for the normal functioning of a number of bodily functions. Functions that require vitamin D include:
Bone building
Maintaining normal calcium levels in the blood and bones
Regulation of nerve impulse transmission
Contribute to the contraction and relaxation of muscles
Regulating the work of the heart and preventing heart disease and diabetes.
Strengthening and supporting the immune system and preventing infectious diseases
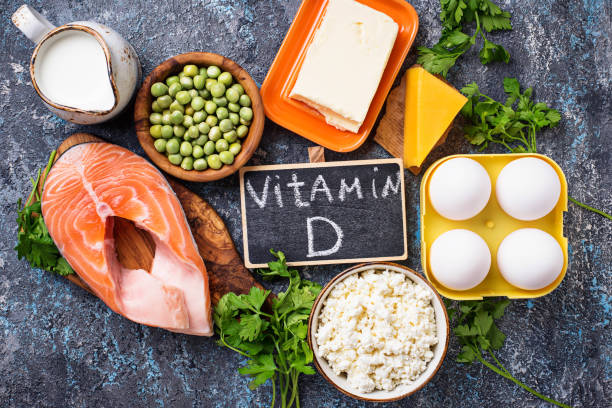
What are the most important sources of vitamin D?
The body obtains most of its need for vitamin D through its own manufacture, starting from cholesterol, during exposure to sunlight and absorption of ultraviolet rays to the skin, and the body gets a small amount of vitamin D from food sources that include:
eggs
the milk
red meat
chicken
Fatty fish such as salmon, tuna and mackerel
How much vitamin D do I need?
The daily requirement of vitamin D for an adult is approximately 600 international units, and the need for vitamin D increases with age and reaches 800 international units per day for the elderly.
The severity of vitamin D deficiency varies according to the level of the vitamin in the body, as:
Can too much vitamin D be harmful?
High vitamin D levels of more than 125 nmol/L lead to vitamin D poisoning, which leads to hypercalcemia, and thus nausea, vomiting, weakness, irregular heartbeat, acute pancreatitis, kidney problems, and bone pain. Therefore, you should not take excessive amounts of vitamin D and stick to the allowed daily dose only.
Causes of vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency occurs due to one of the following reasons:
Not being exposed to the sun enough to synthesize vitamin D in the body
The inability to absorb or synthesize vitamin D due to malabsorption diseases, genetic diseases, or kidney diseases
Not getting enough vitamin D from food.
risk factors
Risk factors for a vitamin D deficiency include:
Brown and black people
age
Living in cold areas with little exposure to the sun
Obesity
Do not eat fish or dairy and milk products
Not getting outside enough or working from home
Chronic kidney disease such as kidney failure, liver disease, or hyperthyroidism
Diseases that lead to malabsorption, such as Crohn's disease and celiac disease
Previous gastric bypass surgery
Using drugs that affect the synthesis of vitamin D, such as statins and steroids
Always use sunscreen when leaving the house, as sunscreen prevents the absorption of ultraviolet rays
What is the most vulnerable group to vitamin D deficiency?
When living in cold and far from the sun, where the summer lasts only for a short period, the levels of vitamin D in the body decrease dramatically, and therefore the residents of these areas, in addition to the elderly and those with chronic diseases, are the groups most vulnerable to vitamin D deficiency and the resulting damages. .
Effects of vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency causes a group of damages that negatively affect the body, and the most important vitamin D damages are:
Low bone density, osteoporosis, and increased risk of fractures
Deficiency of calcium in the blood
Low phosphate in the blood
Arrhythmia
Muscular weakness and fatigue
Malabsorption and nausea
diabetes
Disorders in the transmission of nerve signals
Depression
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency in the body
Vitamin D deficiency in the body causes a wide variety of symptoms that involve a large number of organs and body systems, including:
Psychological symptoms of vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency causes changes in the psychological state, the most important of which is anxiety, tension, and mood changes, as several studies link vitamin D deficiency with anxiety disorders, and other studies in pregnant women prove that the presence of sufficient vitamin D greatly contributes to improving mood, comfort, and getting rid of anxiety. .
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency on the muscles
Vitamin D deficiency causes muscle pain, muscle weakness, difficulty moving, and a lack of muscle contraction. This is because vitamin D is important for maintaining normal levels of calcium in the body, and calcium, in turn, is important for muscle activity and health, for getting rid of energy consumption and preventing muscle fatigue. With a lack of vitamin D, a lack of calcium causes muscle pain, weak contraction, and fatigue.
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency on the skin
Vitamin D deficiency causes a range of symptoms on the skin, which include:
Dry skin and premature skin aging
skin cracks
Hair loss because vitamin D is necessary for the growth of hair follicles
Delayed and poor wound healing
Skin rash, noticing redness and itching with dry skin
young love
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency on the bones
Vitamin D is an essential element in the process of bone formation, bone cell building, and calcium deposition in bones. Without the presence of vitamin D or when there is a deficiency in its levels, bone density will decrease dramatically due to the withdrawal of calcium and phosphate from the bones and their transfer to the blood, which leads to:
osteoporosis
Bone pain
Ease of exposure to fractures and bruises
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency on the nerves
Vitamin D deficiency causes a number of neurological problems, because vitamin D causes calcium deficiency in the blood and calcium is necessary for the completion of neurological functions. Therefore, vitamin D deficiency leads to delayed transmission of nerve signals and to problems including:
Dizziness and fatigue
Poor focus
Impaired memory and cognitive functions
epileptic seizures;
Disorder of consciousness and confusion in cases of persistent severe vitamin D deficiency
The most dangerous symptoms of vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D causes a large number of important signs and symptoms, but the most serious symptoms of vitamin D are those associated with a lack of calcium in the blood, which include:
Heart problems, the most important of which is slow heartbeat and irregular heartbeat
Advanced neurological symptoms such as disturbed consciousness, confusion, coma, and epileptic seizures
Vitamin D deficiency and depression
Vitamin D plays an important role in neurotransmission and electrical signals in the brain. It also regulates the release of psychologically important neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin and helps them bind to cells. Therefore, a deficiency in vitamin D can cause mood disorders, depression, and mental state changes.
Diagnosis of vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency can be diagnosed through blood tests to measure the levels of the vitamin and its derivatives in the blood. In addition, this analysis is not routinely requested, but it is the test by which vitamin D deficiency can be diagnosed.
There are two types of vitamin D that can be measured in the blood, namely:
The primary or inactive type of vitamin, vitamin D2 or calcidiol
The active kind, vitamin D3, or calcitriol
In most cases, blood analyzes are conducted to measure the amount of the inactive type D2, because its levels in the blood are higher and because its stay in the blood is longer, which makes it easier to detect than the active type D3.
Psychological symptoms of vitamin D deficiency
Treating vitamin D deficiency
Treatment of vitamin D deficiency aims to compensate for the deficiency in the vitamin and restore its levels in the body to the normal range. Vitamin D is usually treated using nutritional supplements, and the daily therapeutic dose is determined based on a number of factors, including age, amount of sun exposure, diet, and general condition.
The following doses are given according to the age group:
Children under 1 year: 400 IU per day (10 mcg)
1-70 years: 600 IU daily (15 mcg)
Older adults over 71: 800 IU (20 mcg) daily.
In cases of severe vitamin D deficiency, vitamin D compensation may need medical treatment through vitamin D injections containing 50,000 international units. The patient is given several injections over a period of several weeks, then he follows up with nutritional supplements as before.
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency
Magnesium helps improve vitamin D absorption, so it is possible to give magnesium supplements for treatment.
In addition to replacing vitamin D through medical treatment and nutritional supplements, it is also important to modify the diet to increase the intake of vitamin D-rich foods, which include:
fatty fish
eggs
the milk
red meat
beef liver
Dairy products
Also, continuous exposure to the sun is important in order to increase the production of vitamin D in the body. Going out in the sun for half an hour in the morning every day is beneficial in improving vitamin D levels.
Is vitamin D deficiency transmitted to a Hollywood smile?
Vitamin D deficiency causes calcium deficiency in the body and osteoporosis, which in turn affects the jaw bones and teeth. It increases the risk of periodontal disease, alveolar osteitis, gingivitis, and dental caries. It also helps build up waste products on the teeth and gums, which can damage a Hollywood smile.
Your medical advice to prevent vitamin D deficiency
In most cases, vitamin D deficiency can be prevented by following simple daily steps that include:
Go out in the sun every day for at least half an hour
Eat food rich in vitamin D
Drink enough water to maintain kidney health, as the kidneys are where vitamin D3 is synthesized
Avoid drinking alcohol to protect the liver from damage, as the liver makes the first form of vitamin D (vitamin D2).
